Lake Mead Levels Steady but Troubling Projections Loom for 2027
Lake Mead, one of the largest reservoirs in the United States, has recently been maintaining steady water levels; however, scientists warn that this stability may not last long. Projections indicate that the iconic lake could face alarming record lows by 2027, igniting concerns over water scarcity not only for urban areas but for agricultural sectors that rely heavily on its resources.
The Current Status of Lake Mead
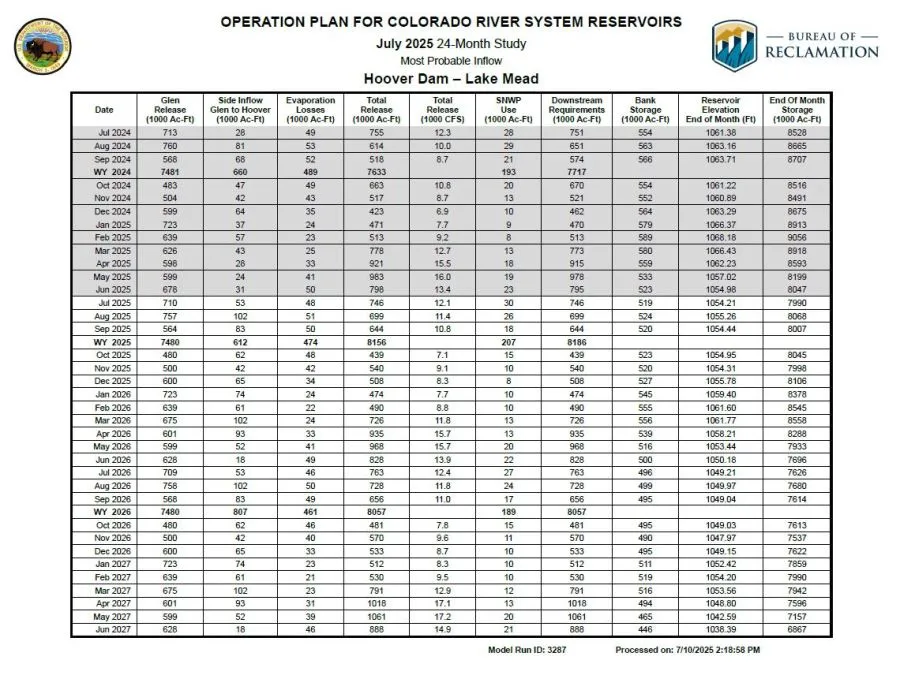
As of now, Lake Mead’s water level has remained relatively stable, thanks in part to seasonal rainfall and water conservation measures. Recent reports show the lake’s elevation hovering around 1,060 feet, a level that is critically low but stable compared to the drastic declines witnessed in previous years.
In 2021, the water level sank to just above 1,067 feet – its lowest since the lake was filled in the 1930s. With the ongoing drought and climate change impacting the Colorado River—its primary water source—scientists have urged immediate attention to the lake’s future and to implement viable water management solutions.
A Pivotal Outlook: What 2027 Could Mean for Lake Mead
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) alongside various climate scientists have detected alarming trends that could lead to severe water shortages in just a few years. Though the lake’s water level is steady for now, models suggest that, without significant intervention, Lake Mead’s level could drop below its current record lows by the year 2027.
The looming concern is attributed to a combination of climate change factors, including decreasing snowfall in the Rocky Mountain region, increased evaporation rates, and water overconsumption from various states that rely on the Colorado River Basin.
Farmers Weighing In: Preparing for Scarcity
Farmers and agricultural stakeholders in the southwestern U.S. are particularly concerned about the forecast for Lake Mead. As a critical water source for irrigation across Arizona, Nevada, and California, any significant drop in water levels could impact crop output and agricultural economics profoundly.
Farmers are already being advised to begin planning accordingly. With the echoes of drought ringing through fields and economic landscapes, agricultural extensions are becoming proactive. Innovations in irrigation technology, crop diversification, and strong advocacy for sustainable practices are among the strategies being employed.
John McCarthy, a representative for the Arizona Farm Bureau, emphasized the importance of foresight. “With predictions suggesting a decline in available water resources, our farmers need to adapt rapidly. It’s not just about survival but ensuring that we can sustain our agricultural productivity,” he stated.
Regional Collaboration: An Urgent Priority
To address the impending crisis, interstate collaboration is more crucial than ever. States that draw from the Colorado River, namely Arizona, California, Nevada, Utah, Colorado, New Mexico, and Wyoming, are in discussions to optimize their water usage and to share resources more effectively.
The Colorado River Compact, established in 1922, allocates water rights to the states, but prevailing arid conditions have led to calls for reevaluation of these allocations. The issues surrounding water rights have been contentious, with each state striving to meet the needs of its residents and industries.
Negotiations have involved voluntary reductions in water use and investment in projects that could bolster water conservation. The aim is to find balance and ensure a more sustainable future for all states involved.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change is the overarching catalyst for this crisis, altering natural weather patterns that significantly affect water availability. Longer droughts and unpredictable weather events frame a bleak picture of the future, particularly for the American Southwest, where populations and agricultural demands continue to grow.
Research shows that climate trends in the region are not likely to abate. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the West is expected to experience ongoing warmer and drier conditions, an alarming prediction for already stressed ecological systems.
Efforts to Promote Water Conservation
Local governments are responding by pushing for water conservation initiatives. Campaigns aimed at promoting water-efficient appliances, xeriscaping in landscaping, and public education on water usage are increasingly becoming part of community programming. Cities such as Las Vegas are leading the charge, placing restrictions on water use for turf and landscaping while encouraging drought-resistant vegetation.
Innovation in technology also plays a critical role in the search for smart water consumption. Advanced irrigation systems equipped with moisture sensors, automated water delivery systems, and cloud-based data tracking for usage are becoming pivotal tools in the fight against excessive consumption and waste.
Looking Ahead: What’s Next for Lake Mead?
The future of Lake Mead hangs in the balance. As scientists and specialists emphasize the critical nature of this situation, potential solutions hinge on cooperation among states, better resource management, innovation, and an earnest commitment to fighting climate change.
As we move closer to the predicted nadir in 2027, the need for action is urgent. Local communities, farmers, industrialists, and policymakers must come together to bolster sustainable practices, advocate for long-term water contracts, and push for more extensive legislation aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change.
While the current stability of Lake Mead may provide a sense of calm, the shadow of future shortages looms large. It is vital for all stakeholders to recognize the seriousness of these reports and strive for a united approach to ensure that Lake Mead remains a vital resource for future generations.
Conclusion
Lake Mead is more than just a reservoir; it is a critical lifeline for millions and an integral part of the American landscape and economy. Its current stability should not be a reason for complacency but rather a call to action. As experts watch closely and prepare for the future, it is essential that communities, farmers, and governments heed these warnings and act now to secure this vital resource for all.